Membres
Une équipe hétéroclite
PUBLICATIONS
Découvrez nos publications
Actualités
Toutes nos actualités
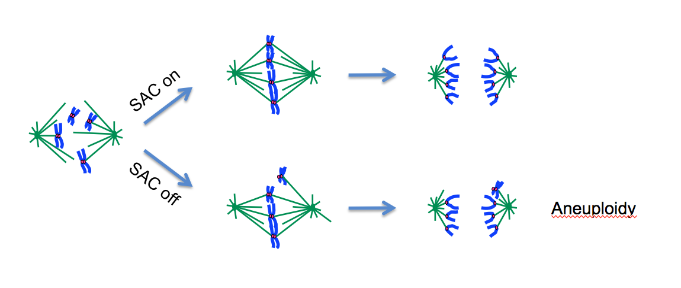
Faithful chromosome segregation during mitosis is essential for the generation of a viable cell progeny, with an identical set of chromosomes at each cell division. Inaccuracies in chromosome segregation lead to abnormalities in chromosome number, known as aneuploidy, a major cause of spontaneous miscarriages and birth defects, and a hallmark of human cancers. In eukaryotic cells a highly conserved surveillance system, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), operates during mitosis to delay mitotic progression under conditions that could compromise accurate chromosome segregation. During mitosis, spindle checkpoint components are recruited to unattached kinetochores and produce an inhibitory signal that blocks the E3 ubiquitin ligase, APC/C. When all kinetochores acquire stable bipolar attachments, the checkpoint is quickly and irreversibly switched off, leading to APC/C activation and ubiquitination of several mitotic substrates, allowing anaphase onset and mitotic progression. Our team is interested in better understaning the mechanisms underlying mitotic progression and its regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint and to evaluate the plasticity of those processes and how they can be modified to adapt to the different requirements associated with eukaryotic diversity.
Une équipe hétéroclite
Découvrez nos publications
Toutes nos actualités
Despite the essential role of the spindle assembly checkpoint in somatic cells, work in frog, worm and fish embryos has shown that microtubule perturbations that lead to erroneous kinetochore-spindle associations do not block mitosis during early embryogenesis, suggesting that the SAC is relaxed in early metazoan embryos…
The machinery that drives mitosis and its control through the spindle checkpoint is conserved across many eukaryotes. However, our understanding of chromosome segregation and its control derives almost entirely from few intensively studied model organisms….

Laboratoire de Biologie du Développement UMR 7009
Cette UE se déroule sur 2 semaines et a lieu au laboratoire de Biologie du Développement de Villefranche -sur-Mer (LBDV). Elle inclut l’examen de l’UE d’analyse scientifique (5V089) suivie par les étudiants de la spécialité de Biologie du Développement.
Durant la 1ère semaine, les étudiants participent à des ateliers et des rencontres avec les chercheurs du laboratoire.
Durant la 2ème semaine, les étudiants sont répartis dans les équipes pour y réaliser un mini projet qu’ils présentent le dernier jour du cours. Le cours est donné en anglais pour tout ou partie.
Modalités d’évaluation
Présentation orale du mini-projet (binôme, 100 %)
UE en anglais (partiellement ou totalement)
Master BMC, S3, 6 ECTS
Code UE: 5V200
Responsable de l’UE: Carine BARREAU (MCU): carine.barreau [at] obs-vlfr.fr
Cette UE permet aux étudiants de 1ère année de Master de passer 2 semaines à l’Observatoire Océanologique de Villefranche-sur-Mer. Le cours est obligatoire pour les étudiants du Master Biologie Intégrative, parcours Biologie et Bioressources Marines (BBMA) tandis qu’il peut être choisi en option par les étudiants du Master Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire (BMC). Les étudiants participent à des ateliers de présentation des organismes marins utilisés par les équipes de recherche du laboratoire (LBDV) et apprennent à les manipuler au cours de travaux pratiques dont les thématiques vont de la Biologie du Développement fondamentale à la toxicologie appliquée.
Modalités d’évaluation
Analyse d’article et présentation orale (50%)
Compte-rendu écrit de TP (50%)
UE partiellement en anglais
Master BIP, S2, 6 ECTS
Code UE: 4B022 (ouverte au Master BMC)
Responsable de l’UE: Carine BARREAU (MCU): carine.barreau [at] obs-vlfr.fr
Cette UE complémentaire se déroule sur 2 semaines et permet aux étudiants de découvrir les différents aspects (métiers & recherche) de l’Observatoire Océanologique de Villefranche-sur-Mer (OOV). Ateliers et journal clubs sont organisés afin que les étudiants mettent en pratique leurs connaissances théoriques en biologie et développent leur capacité de communication scientifique en français et en anglais.